The goal of user research
THE PROBLEM YOUR SOLVING IS:
You're solving for the lack of information that you, your team, and company have.
INFORMATION TO LOOK FOR
• Capture & explore reactions
• Identify/explore behaviors & needs
• Shine light on & identify the unknowns
• Better understand the known, unknowns (points we know that we don't know enough about)
• Further validate/understand the known, knowns (points we do know that about)
ACTIVITIES
• List your important assumptions to validate or invalidate & why
• Understand what is important for you to learn about & why (learning goals)
• Go gather insights and learn about the people targeting
• Look for patterns of information that helps us better understand our learning goals.
• Identify patterns of information that validate/invalidate our assumptions, problems were solving & solution assumptions
• Developing an understanding of the user’s mental model = “information order = make the design more intuitive”
• 5-7 people is a good starting point to get going

How to build a user interview script
The goal is to have a natural discussion that feels human, not just sound like a robot, and answer all your questions.
TWO TYPES OF INTERVIEW SCRIPTS

The topic map example
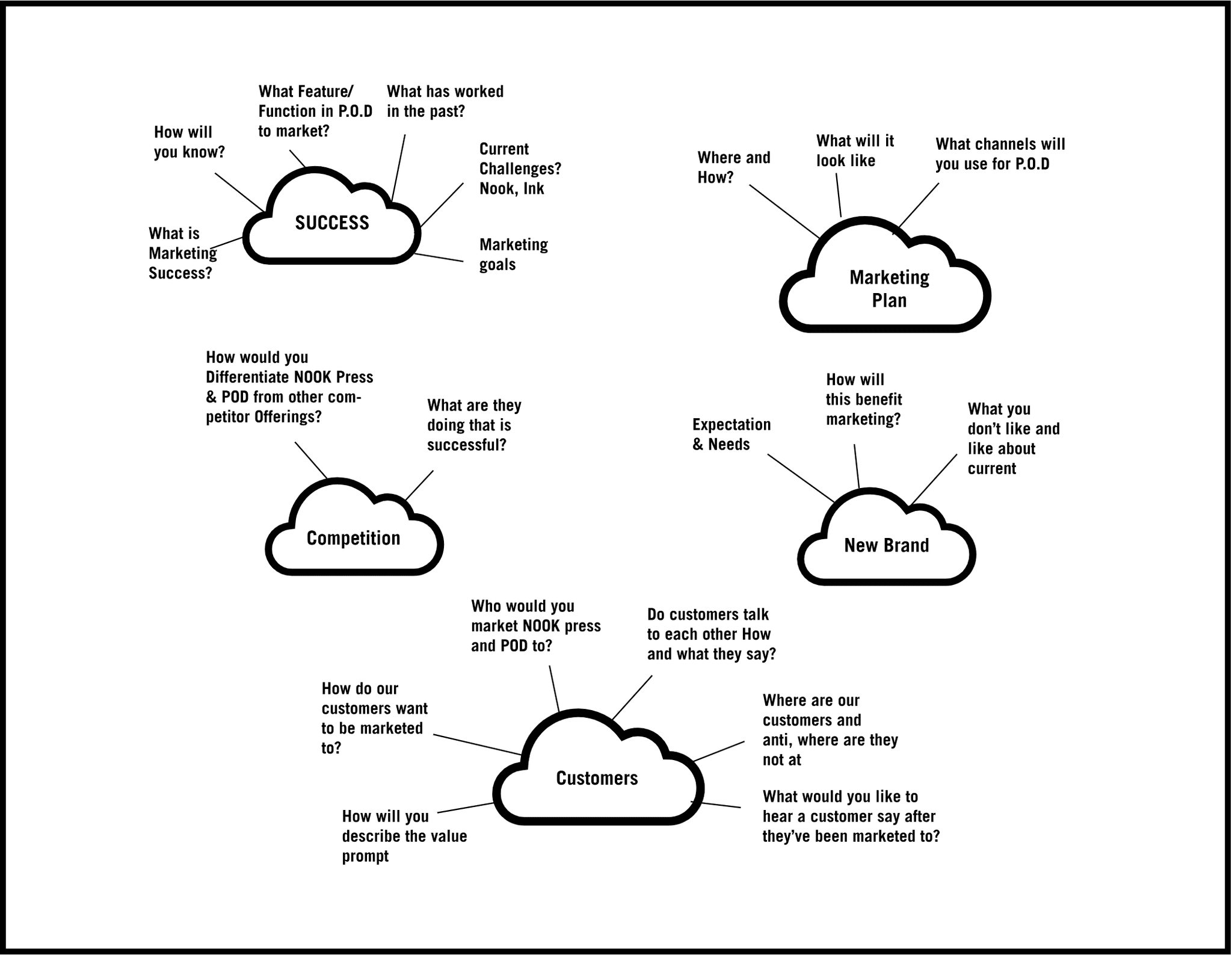
Building an interview script
1
Start with identifying your learning goals and/or assumptions.
EXAMPLE OF LEARNING GOALS
• College Preference = How do students make decisions on which college they want to apply for
• Application Process Improvements = What can be improved regarding the application process
• IxD Program Preference = Why did our students choose the IxD department for their degree
EXAMPLE OF ASSUMPTIONS
• Online reviews are the most important data points that students look for when making
decisions on which colleges to apply for.
• Students find our application process has too many questions that are not helpful.
• Students chose the IxD program because it has the most diverse set of technology skills to learn.
2
Write questions that help you learn more about your learnings goals or validate/invalidate your assumptions.
EXAMPLE OF QUESTIONS
College Preference (learning goal)
Q. Did you look at other colleges before deciding on AAU?
Q. If yes, What were the other colleges that you looked into and why?
Q. If no, why not?
Q. What is most important to research and review when it comes to selected a college?
Q. Was there a time where you looked at online reviews or peer reviews regarding a specific college?
Q. If yes, where do you go to find online reviews and how helpful are reviews in general?
Q. If both, which review would you prioritize as being the most helpful online or peer, and why?
Q. If you can choose 1 thing, what was the most important data point that triggered you to go with AAU?
Q. Any other reasons why you chose AAU?
Q. Are you happy with your choice so far? Follow up with why…
Q. Looking back, was there anything AAU could have done to further make this decision process easier?
3
After writing questions,
place them into the interview script
format in the order that feels best to start
the conversations or interview structure.
SETTINGS PAGE
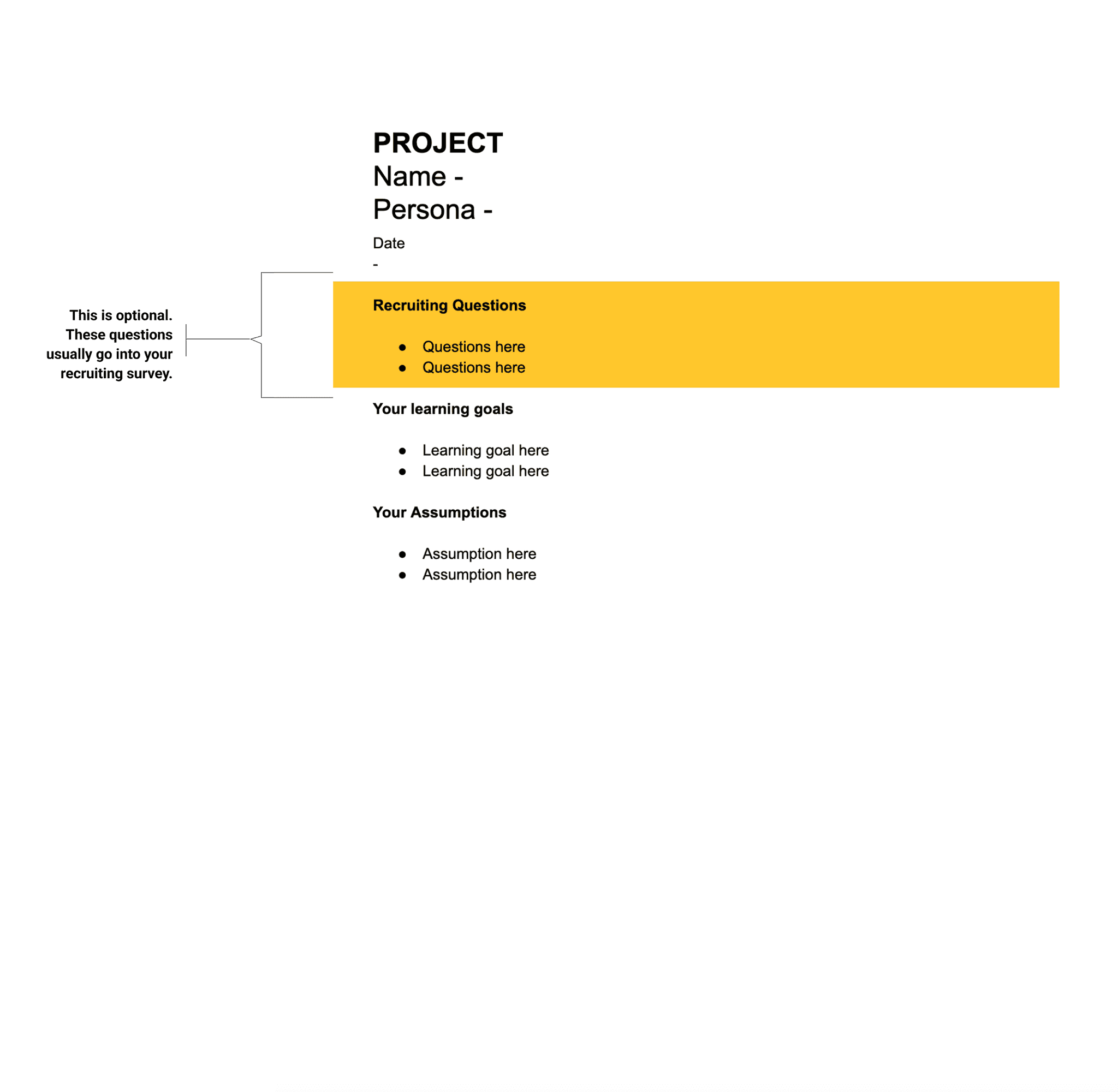
INTRODUCTION PAGE

QUESTIONS PAGES
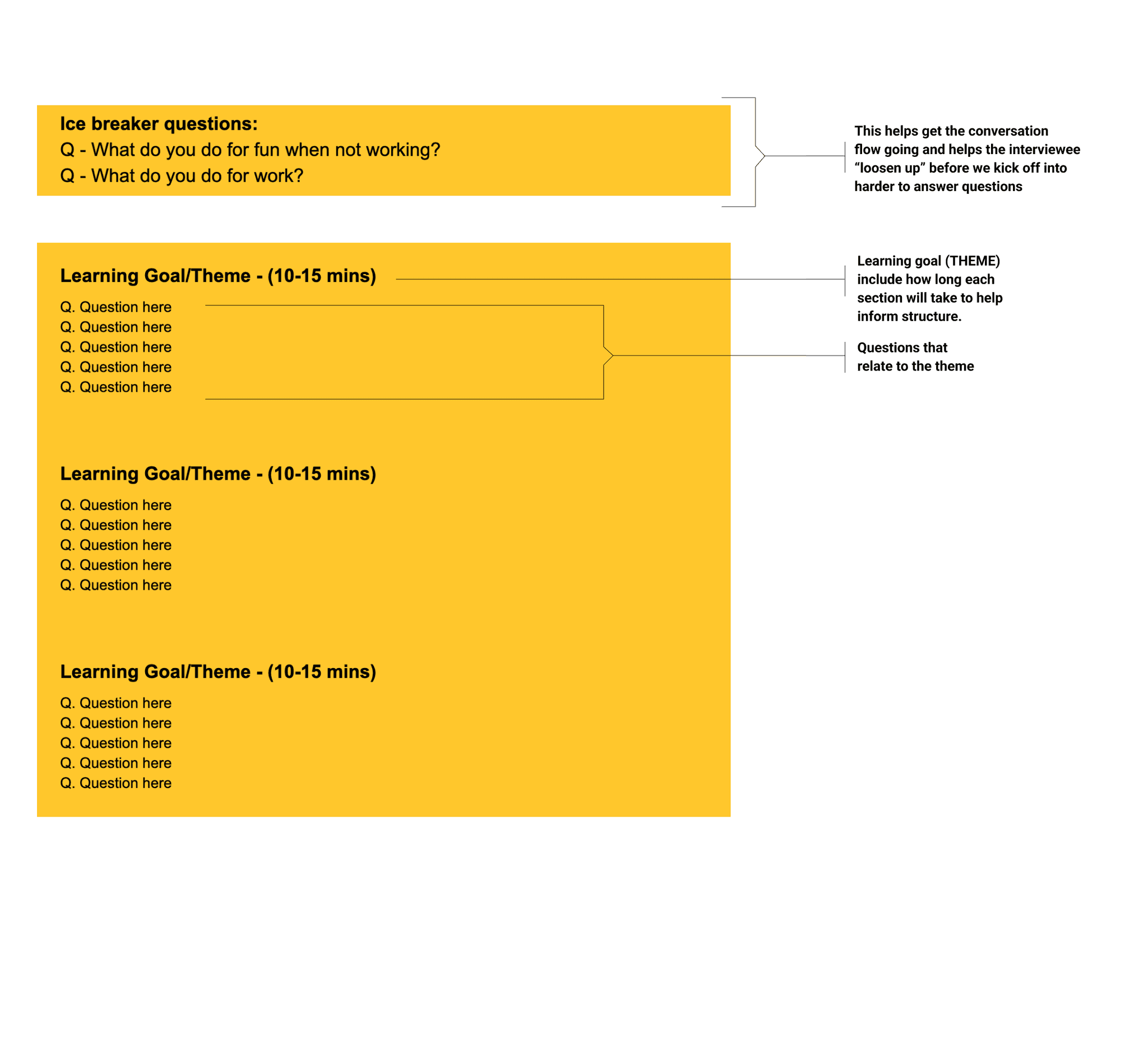
OUTRO SECTION
Download Interview Script Template
Writing a question best practices
WHAT MAKES A GOOD QUESTION?
• A good question, tells a good story...
• In that story, you get human behavior.
• You want to learn about problems & the experiences around the problems.
• Think about the persona framework: Needs/Goals, Behaviors/Activities, Pains
• Avoid leading questions
WHAT IS A LEADING QUESTION?
A leading question prompts or encourages as desired answer.
Example: You we're in LA last week right? vs Where were you last week?
FRAMING QUESTIONS
Start high level & opened ended
Don't do this:
What do you use your Ipad for?
Why is this question not good?
It assumes too much—assumes someone uses an ipad
Start high-level & open ended, which will allow for you to learn much more:
How do you engage with technology? = Story
What do you use the most? = Importance
Why is do you use your ipad the most? = Activities/Needs
What are the most common reasons you use your ipad for? = Activities/Needs
How often and what triggers you to usually use your ipad? = Behaviors
Is there any problems/friction that you experience, if so please describe in detail? = Problems/Needs
Spark conversations around
• Scenarios/Activities
• Real World Context
• Pains & Joys
• First Time & Most Recent Time
• Best Time & Worst Time
• Wish List
Conversation prompts
• Have you ever had an experience where (describe a scenario)?
• Can you tell me that story from beginning to end?
• And then what happen?
• Why (or how) did you do that?
• What did you love most about that?
• What did you not like about that, if any?
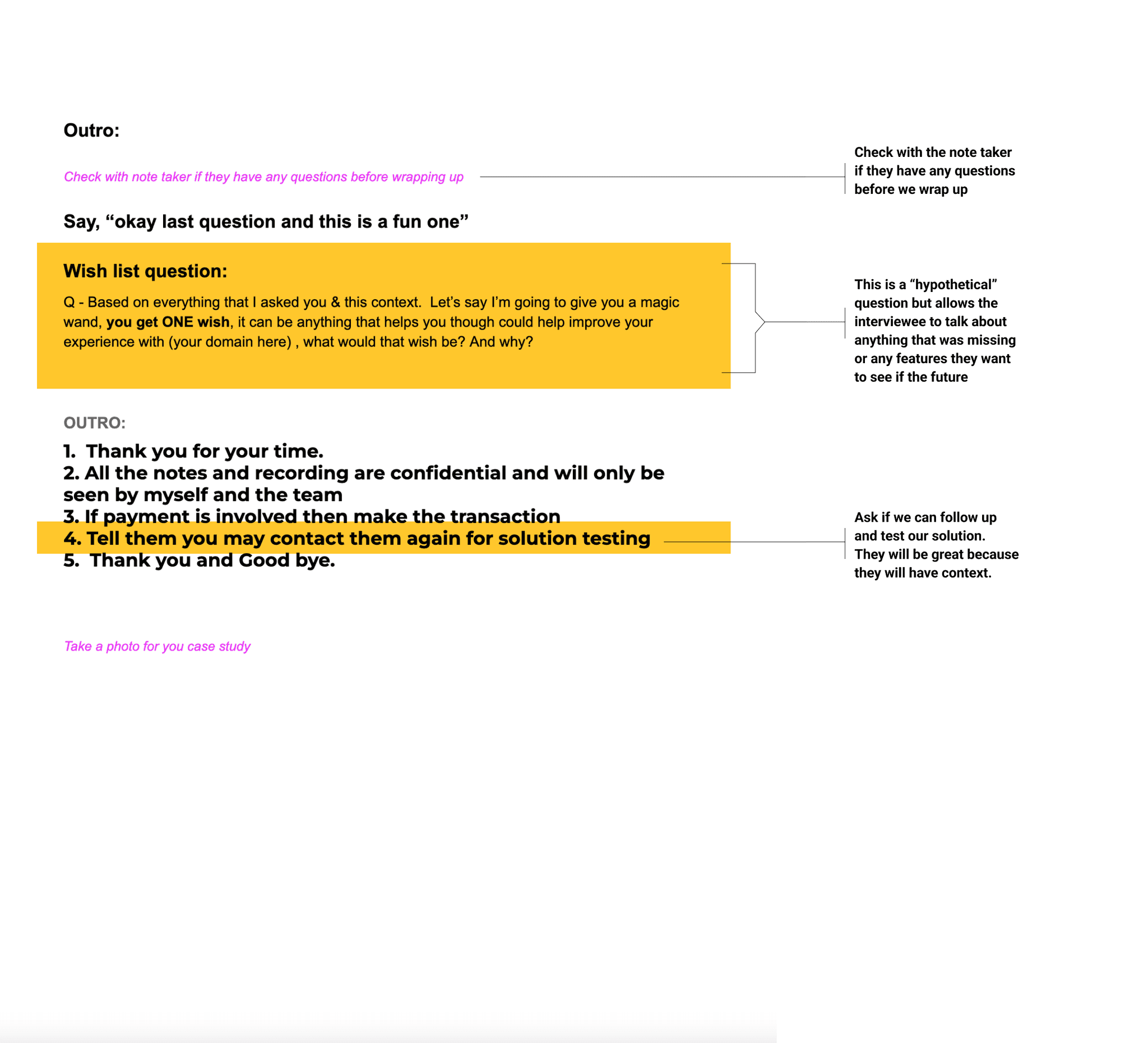
• If I can give you a magic wand, you get one wish— what would you improve regarding that experience and how would you improve it?
Tip:
Start your questions with why, what, where, how = Stories
Start your questions with do & is = yes & no answers
During the interview, it's best to:
• Smile
• Ask open ended questions
• Get their story
• Ask about past & current behaviors
• Be quiet & listen
• Ask why, how, what, when, where
During the interview, don't do:
• Talk about your product
• Talk the entire time
• Ask leading questions
• Ask about future behaviors!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
• Say, do you like it or would you use "product here"
• Don't cut people off unless absolutely necessary
• Sell
• Ask lots of yes & no questions that don't follow up
Follow this strategy called the "deep dive" when listening to someone tell the story:
Get their story first, then go back and dive into the areas that you wanted to when they were first telling you the story. Essentially, don't cut people off when their telling you a story from beginning to end.
